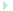CPUThe CPU Unit (a home-made multi-cards frame) has two buses in the backplane: the A-BUS (16 address lines) and the D-BUS (8 data lines). Different cards connect to those buses. Other connections such as internal control signals also exists between cards. The U-BUS is the external bus; only the "Bus Controller Card" is connected to it. The U-BUS is not present in the backplane.
The CPU architecture is pretty classical. The register A (accumulator) serves as left operand and result for the ALU. It is not possible to obtain ALU results in a register other than A. What it is possible, however, is to transfer data between 8-bits and 16-bits registers using instructions such as: "movh b, y".
The register MB (Memory Bank) provides support for a memory banking scheme allowing for 16 MB of memory divided in 256 banks of 64KB each. Note that the internal address bus (A-BUS) is 16 bits so the banking scheme is optional and has no impact to the rest of the architecture.
There is not MDR/MAR registers but a 16-bits MDAR register which sole mission is to hold the operand for immediate and direct addressing modes instructions. The Instruction Decoder and Sequencer (IDS) is hard-wired (no micro coded) implemented with PLD chips.

|
|
Homebuilt CPUs WebRing
JavaScript by Qirien Dhaela
Join the ring?
David Brooks, the designer of the Simplex-III homebrew computer, has founded the Homebuilt CPUs Web Ring. To join, drop David a line, mentioning your page's URL. He will then add it to the list.
You will need to copy this code fragment into your page.
Project start date: May 13 of 2009
|